Blog
Understanding Tube Fuses: A Comprehensive Guide to Selection
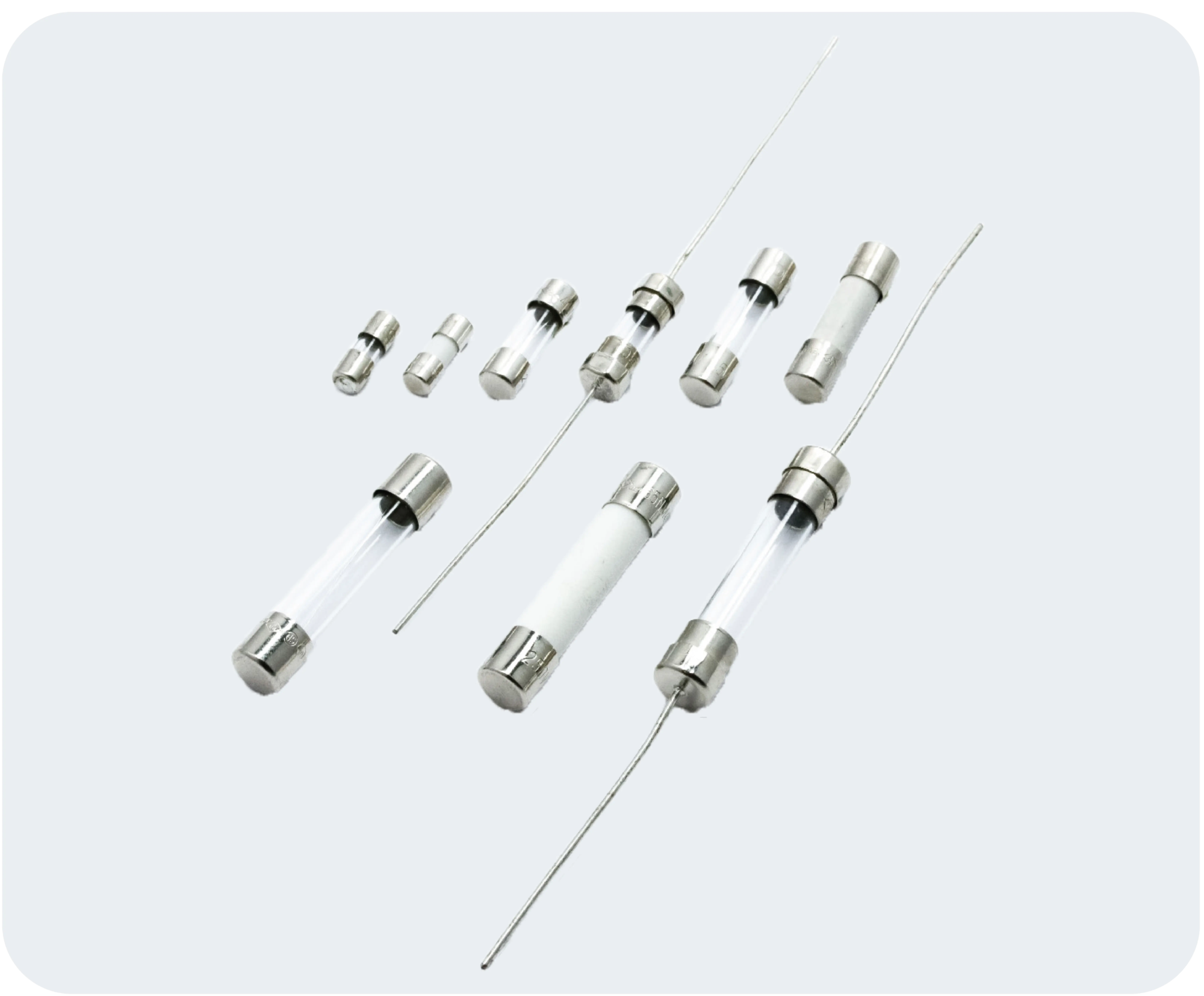

Tube fuses have been a cornerstone of circuit protection for decades, offering reliable and efficient safeguarding against electrical overloads and short circuits. These versatile devices play a crucial role in various industries, from automotive to industrial applications. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the intricacies of tube fuses and provide you with the knowledge to make informed decisions when selecting the right fuse for your specific needs.
The Evolution and Importance of Tube Fuses
Tube fuses have a rich history dating back to the early days of electrical systems. Their simple yet effective design has stood the test of time, evolving to meet the increasingly complex demands of modern electrical and electronic devices.
Historical Context
The concept of fuses dates back to the 19th century when electricity was first being harnessed for commercial and residential use. Early fuses were simple devices, often just a piece of wire that would melt when subjected to excessive current. As electrical systems became more sophisticated, so did the fuses designed to protect them.
Tube fuses, characterized by their cylindrical shape and ability to be easily replaced, gained popularity in the early 20th century. They offered a standardized approach to circuit protection, allowing for easier maintenance and replacement across various applications.
The Role of Tube Fuses in Modern Systems
Today, tube fuses continue to play a vital role in protecting electrical circuits and equipment. They serve as a “weak link” in the electrical system, designed to fail safely when exposed to overcurrent conditions, thereby preventing damage to more expensive components or potential fire hazards.
Key benefits of tube fuses include:
- Simplicity: Their straightforward design makes them easy to understand and replace.
- Reliability: When properly selected, tube fuses provide consistent and dependable protection.
- Cost-effectiveness: Compared to more complex circuit protection devices, tube fuses are often more economical.
- Variety: Available in a wide range of sizes, ratings, and response times to suit diverse applications.
Understanding Tube Fuse Basics
Before delving into the selection process, it’s essential to understand the fundamental characteristics and components of tube fuses.
Anatomy of a Tube Fuse
A typical tube fuse consists of several key components:
- Fuse element: This is the heart of the fuse, typically a metal wire or strip designed to melt when subjected to excessive current.
- Fuse body: Usually made of glass or ceramic, the body encases the fuse element and provides insulation.
- End caps: Metal caps at each end of the fuse body serve as connection points and often include rating information.
- Filler material: In some fuses, a filler material surrounds the fuse element to help quench the arc when the fuse blows.
How Tube Fuses Work
The operation of a tube fuse is based on a simple principle:
- Under normal conditions, the fuse element carries the current without interruption.
- When an overcurrent occurs, the fuse element heats up.
- If the overcurrent persists, the element melts (or “blows”), creating an open circuit.
- This open circuit interrupts the flow of electricity, protecting the rest of the circuit from damage.
Key Factors in Tube Fuse Selection
Selecting the right tube fuse involves considering several critical factors. Let’s explore each in detail:
1. Nominal Current Rating
The nominal current rating, often referred to as the ampere rating, is the amount of current the fuse can carry continuously without interruption. This rating should be selected based on the normal operating current of the circuit being protected.
Selection tip: Choose a fuse with a nominal current rating slightly higher than the normal operating current of the circuit. This prevents nuisance tripping while still providing adequate protection.
2. Voltage Rating
The voltage rating of a fuse indicates the maximum voltage at which it can safely interrupt a fault current. It’s crucial to select a fuse with a voltage rating equal to or higher than the maximum voltage of the circuit.
Selection tip: Always err on the side of caution by selecting a fuse with a voltage rating higher than your circuit’s maximum voltage.
3. Interrupting Rating
The interrupting rating, also known as the breaking capacity, is the maximum fault current that the fuse can safely interrupt without rupturing. This rating is critical for ensuring the fuse can handle potential short-circuit currents in the system.
Selection tip: Consult with an electrical engineer or refer to system specifications to determine the potential fault currents in your application, and choose a fuse with an adequate interrupting rating.
4. Time-Current Characteristics
Fuses have different time-current characteristics, which describe how quickly they respond to overcurrents. These are generally categorized as:
- Fast-acting: Respond quickly to both small and large overcurrents.
- Time-delay: Can withstand temporary overloads but still respond quickly to short circuits.
- Very fast-acting: Designed for sensitive electronic equipment, these fuses respond extremely quickly to overcurrents.
Selection tip: Consider the load characteristics of your application. For circuits with motor loads or other devices with high inrush currents, time-delay fuses may be more appropriate to prevent nuisance tripping.
5. Physical Size and Mounting
Tube fuses come in various physical sizes, often standardized for specific applications. Common sizes include:
- 5x20mm
- 6.3x32mm
- 1/4″ x 1-1/4″
Selection tip: Ensure the fuse you select fits the existing fuse holder or clip in your application. Consider both the diameter and length of the fuse.
6. Environmental Factors
The operating environment can significantly impact fuse performance. Consider factors such as:
- Temperature extremes
- Humidity
- Vibration
- Altitude
Selection tip: For harsh environments, consider fuses with ceramic bodies, which generally offer better resistance to extreme conditions compared to glass-bodied fuses.
7. Agency Approvals and Standards
Depending on your application and industry, specific agency approvals or compliance with certain standards may be required. Common standards include:
- UL (Underwriters Laboratories)
- CSA (Canadian Standards Association)
- IEC (International Electrotechnical Commission)
Selection tip: Verify that the fuses you select meet all necessary regulatory requirements for your specific application and region.
Special Considerations for High-Performance Applications
In some high-performance or critical applications, additional factors may need to be considered:
Nominal Melting I²t
For applications where the fuse must sustain large current pulses of short duration (such as in some power supplies or motor start circuits), the nominal melting I²t should be analyzed. This value represents the energy required to melt the fuse element and is useful for coordinating protection in systems with multiple fuses.
Selection tip: Work with the fuse manufacturer to obtain detailed I²t curves for the fuses you’re considering, and compare these with the expected pulse characteristics of your application.
Voltage Drop
In low-voltage or high-precision applications, the voltage drop across the fuse during normal operation may be a concern. Different fuse designs can have varying resistance values, which affect the voltage drop.
Selection tip: If voltage drop is critical in your application, look for fuses specifically designed for low voltage drop, or consult with the manufacturer for detailed resistance specifications.
Industry-Specific Considerations
Different industries may have unique requirements or preferences for tube fuses. Here are some examples:
Automotive Applications
- Often use blade-type fuses rather than glass tube fuses
- May require SAE (Society of Automotive Engineers) approval
- Must withstand vibration and temperature extremes
Electronics and Telecommunications
- May require very fast-acting fuses to protect sensitive components
- Often use smaller form factors (e.g., 5x20mm)
- May need to meet specific telecom standards (e.g., GR-347)
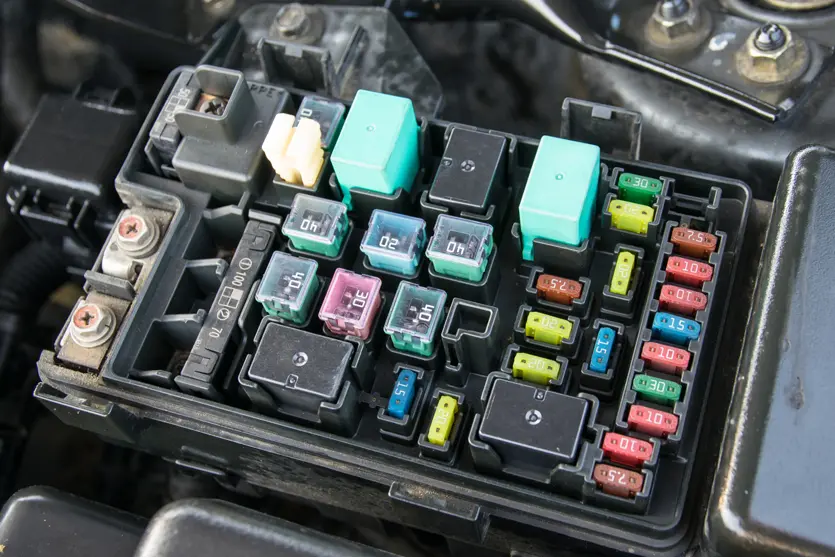
Industrial and Power Distribution
- Often require higher voltage and current ratings
- May need to coordinate with other protective devices in the system
- Might require specific features like indicators for blown fuses
The Role of Eaton Bussmann Fuse Relay in Modern Protection Systems
While this guide focuses on tube fuses, it’s worth noting the advancements in circuit protection technology. Eaton Bussmann, a leader in the field, offers fuse relay products that combine the fast-acting protection of fuses with the convenience of a relay system. These devices can provide:
- Enhanced protection capabilities
- Easier system integration
- Advanced diagnostic features
When considering tube fuses, it’s worth exploring whether more advanced protection solutions like fuse relays might be appropriate for your application.
Best Practices for Tube Fuse Selection and Maintenance
To ensure optimal protection and longevity of your electrical systems, consider these best practices:
- Document your selection process: Keep records of why specific fuses were chosen for each application.
- Standardize where possible: Try to use a limited number of fuse types across your facility to simplify inventory and maintenance.
- Never substitute: Always replace blown fuses with identical ratings and types.
- Regular inspections: Periodically inspect fuses and holders for signs of degradation or damage.
- Training: Ensure maintenance personnel are trained in proper fuse selection and replacement procedures.
- Spare stock: Maintain an adequate supply of spare fuses to minimize downtime.
Conclusion: Making an Informed Decision
Selecting the right tube fuse is a critical task that requires careful consideration of multiple factors. By understanding the key characteristics of tube fuses and the specific requirements of your application, you can make an informed decision that ensures reliable circuit protection.
Remember, while this guide provides a comprehensive overview, complex or critical applications may require consultation with electrical engineers or fuse manufacturers to ensure optimal protection. Always prioritize safety and compliance with relevant standards and regulations.
As technology continues to evolve, stay informed about the latest developments in circuit protection. While tube fuses remain a reliable and cost-effective solution for many applications, new technologies like the Eaton Bussmann fuse relay systems may offer additional benefits for certain scenarios.
By carefully evaluating your needs and staying up-to-date with industry trends, you can ensure that your electrical systems remain well-protected, efficient, and reliable for years to come.
For more detailed information on tube fuse selection and application, consider exploring educational resources and manufacturer guidelines.